CBL-514 Injection
CBL-514 Market value
US$130B2030 Global local fat reduction
market
2030 Global Dercum’s disease market
2030 Global cellulite treatment market
- First-in-class lipolysis injectable that can induce fat cell apoptosis without causing necrosis or damage to other tissues or cells.
- The world's only injectable designed for localized fat reduction in large treatment areas such as the abdomen and thighs.
- Demonstrates favorable safety and tolerability profiles, with mild side effects, no sequelae or systemic side effects.
- Delivers significant results after just one treatment, effectively reducing subcutaneous fat in the treated area.
- Achieved an average reduction of 312.1 mL of subcutaneous fat in the treated area, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to liposuction and other non-surgical fat reduction therapies.
Indications
- Non-Surgical Fat Reduction
- Dercum’s Disease
- Cellulite
Stage
Non-Surgical Fat Reduction
Market Overview
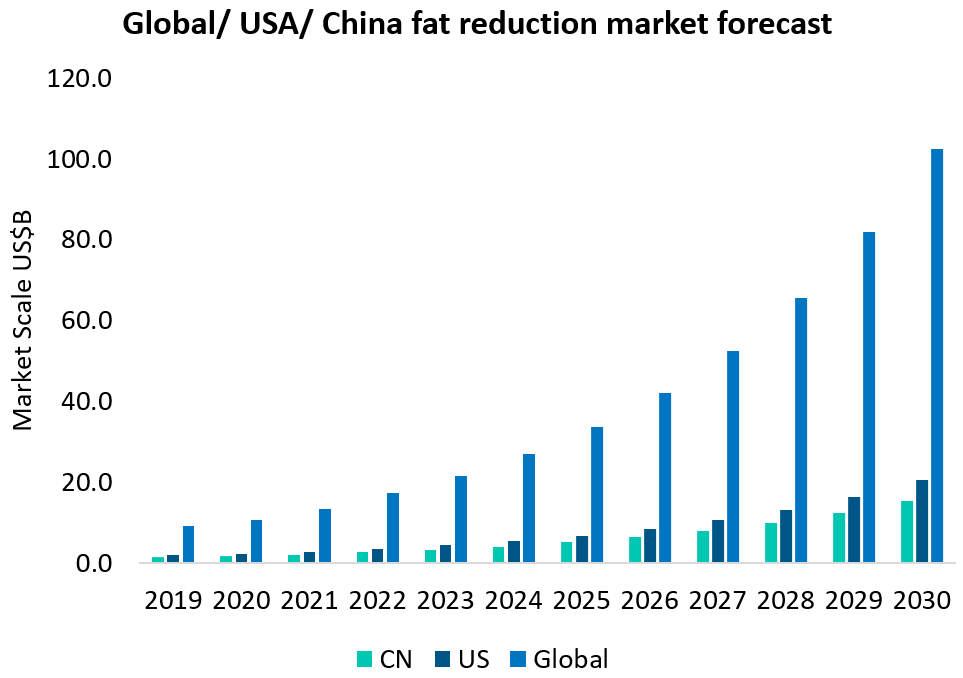
According to the 2021 Deloitte China Body Sculpting Market Industry Development White Paper, China’s local fat reduction and body sculpting medical aesthetic market, including invasive and non-invasive medical treatments, will exceed US$1.5 billion in 2020 and have a CAGR of 25%. It is estimated that by 2030 China market will reach US$15.4 billion, and the global market will reach US$42 billion in 2026, and US$102.5 billion in 2030.
Introduction to Body Fat Reduction Treatments
According to the latest survey data from 2020 American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (ASDS), the number of consumers receiving body sculpting treatment in 2019 increased by 60%, compared with the previous year, and among them, the number of those who sought non‐invasive treatment increased by about 47%. Moreover, American Society for Aesthetic Plastic Surgery (ASAPS) indicates that the number of invasive and non-invasive lipolysis treatments performed in the US increased respectively by -0.4% and 8.2%, compared with 2019. This shows the trend that consumers are gradually turning to non-invasive local fat reduction treatments.
The current subcutaneous fat reduction procedures include invasive surgery, such as liposuction and abdominoplasty, and non-invasive products. Studies have shown that liposuction can remove an average of 183.3mL of abdomen fat, yet it involves a lengthy procedure that is generally performed in an operating room and may also carry the risk of unfavorable outcomes and moderate to severe side effects. The efficacy of non-invasive procedures is generally less optimal with limited treatment areas and potential side effects, including tissue necrosis, nerve damage, and paradoxical adipose hyperplasia (PAH).
According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons’ report, more than 60% of people are reluctant to undergo subcutaneous fat reduction procedures due to the fear of the side effects. The medical needs for subcutaneous fat reduction remain unmet.
R&D Progress
CBL-514 is a 505(b)(1) small-molecule new drug and the world’s first investigational injectable therapy specifically designed for large-area localized fat reduction. Its mechanism of action involves inducing adipocyte apoptosis and lipolysis, effectively reducing subcutaneous fat in the treated area without causing necrosis or damage to surrounding tissues.
Administered via subcutaneous injection, CBL-514 has demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile, enabling significant localized fat reduction without surgery and delivering results comparable to liposuction.
For the aesthetic indication of non-surgical fat reduction, CBL-514 has completed two Phase 2b studies (CBL-0204 and CBL-0205) and is expected to initiate subject recruitment fo two pivotal global Phase 3 studies in the second half of 2025.
- According to the results of our second and the last Phase 2b study (CBL-0205), over 75% of participants achieved at least a 1-grade improvement on the Abdominal Fat Rating Scale (AFRS) at Week 4 post-treatment (p < 0.00005). The use of AFRS also reflects Caliway’s alignment with the U.S. FDA-recommended primary endpoint for future Phase 3 studies. The outcome was consistent with results from the previous Phase 2b study (CBL-0204), demonstrating the consistency of CBL-514’s efficacy, safety, and tolerability.
- In the CBL-0204 study, nearly 60% of participants achieved at least a 1-grade improvement on the AFRS after only one CBL-514 treatment.
- Additionally, data from CBL-0202 stage 2 phase 2 study showed that nearly 70% of participants reduced ≥ 150 mL of subcutaneous fat in the treated area, while over 60% reduced ≥ 200 mL, demonstrating surgical-level efficacy with a significantly better safety profile than liposuction.
CBL-514 remains the only investigational drug globally designed for large-area localized fat reduction. If approved, it is expected to fulfill the substantial unmet need in localized fat reduction and offer a novel non-surgical option for precise body contouring.
Dercum’s Disease
Market Overview
The U.S. market for Dercum's disease in 2019 was approximately US$3.74 billion (approximately one-third of the world), and the global market is estimated to be approximately US$10.9 billion. It is estimated that the global market will reach US$17.7 billion in 2026 with a CAGR value of 7.1%.
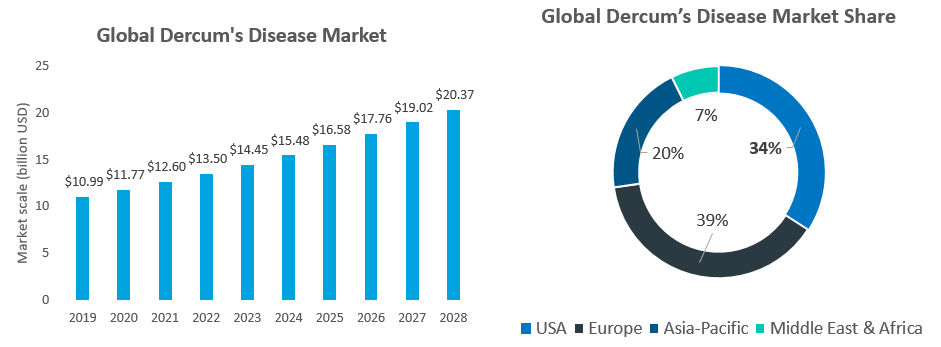
Note: The US market value is estimated by the USA prevalence(124,500) * lipoma treatment avg cost (US$2,000)
Introduction to Dercum’s Disease
Dercum’s disease is a rare disease characterized by painful lipomas with abnormal accumulation of subcutaneous fat in some parts of the patient's trunk, accompanied by severe spontaneous pain in this part. The nature of the pain is acupuncture-like or knife-cutting sharp pain, which is paroxysmal or persistent. It is estimated that approximately 200,000 people in the United States suffer from Dercum’s disease. The cause of this sinus root's disease has not yet been determined. Studies have pointed out that it may be related to nervous system dysfunction, mechanical pressure on nerve tissue, and adipose tissue metabolism disorder.
Currently, there is no approved drug for Dercum’s disease; therefore, surgery and analgesics are the major means to relieve symptoms. However, the efficacies of the current treatment are rather poor and temporary. On the other hand, surgical resection and liposuction come with multiple side effects and sequelae; moreover, they often cause lipoma recurrence.
| Existing Therapies | Surgical Excision (e.g., lipoma removal surgery, liposuction) | Analgesics | Immunomodulators | |
| Purpose | Removing lipomas and pain relief | Pain relief | Reduce inflammation | Pain relief |
| Disadvantage | Deep and large wounds, long recovery, high recurrence and risk of symptom exacerbation | Unable to reduce lipoma size, short-term pain relief only, severe side effects | Poor efficacy with significant systemic side effects | Temporary pain relief, unable to cure the disease |
| Side Effect | Pain, bruising, infection, redness, swelling, and lumps and scarring. |
Apprehension, dizziness, drowsiness, etc. | Headache, tiredness, diarrhea, upset, stomach, infection, hyperhypersensitivity. | Burning sensation, redness, or irritation at the treatment site |
R&D Progress
CBL-514’s indication for treating Dercum’s disease (DD) is under investigation. In previously completed studies, CBL-514 was also observed to induce apoptosis in lipoma cells, suggesting its potential as a treatment for Dercum’s disease.
- The CBL-0201DD Phase 2 study, approved by the U.S. FDA and completed in April 2023, met all primary and secondary endpoints, and demonstrated that CBL-514 is the first and only product to show clinically meaningful and statistically significant results in painful lipomas reduction—with nearly 60% of target lipomas showing either complete clearance or >50% reduction in size, and improve pain significantly by 4.7 points on a 10-point scale (with higher scores indicating greater pain severity).
- CBL-514 was granted both Fast Track Designation and Orphan Drug Designation by the U.S. FDA. In November 2024, it was also granted Orphan Drug Designation by the European Medicines Agency (EMA)—making it the only investigational drug globally to receive both designations for this indication. These regulatory milestones are expected to accelerate future drug approval and review processes.
- The follow-up CBL-0202DD Phase 2b study is currently ongoing in the United States, with topline results anticipated in Q3 2026.
Expanded Access Policy
Currently, CBL-514 is in clinical development stage, which means more clinical studies are required and health authorities have not yet approved the product to be an accredited treatment for Dercum’s Disease.
Caliway encourages clinicians and patients to participate in a clinical trial as the best option for patients to access investigational products. However, we understand that some individuals may not satisfy all the eligibility conditions required to enter a clinical trial, and some may have failed all treatments known to treat their conditions. These patients may receive investigational drug through another option commonly known as “Expanded Access” or “Compassionate Use”.
Generally, Caliway does not provide investigational drugs to patients until there is sufficient data on the safety and efficacy of our products to allow patients and physicians to assess the risks and benefits of using these investigational drugs outside of a clinical trial context. Therefore, after careful consideration, Caliway is not currently offering Expanded Access to CBL-514.
You can find additional information about ongoing clinical trials of CBL-514 on our website and by accessing https://clinicaltrials.gov.
Cellulite
Market Overview
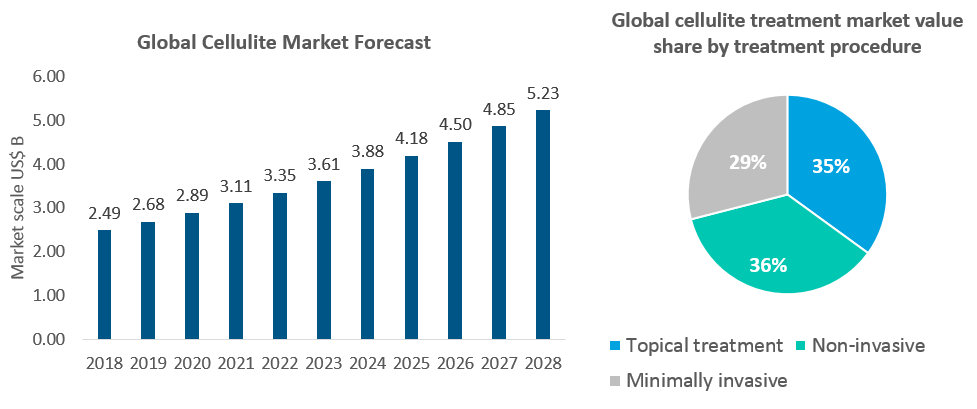
According to the Future Market Insights report, the global cellulite treatment market size was approximately US$2.49 billion in 2018, and it is estimated to reach US$4.5 billion in 2026. According to foreign studies, about 85% of women after puberty have cellulite problems, and with the increase of age and obesity, the probability of obtaining cellulite becomes higher and higher.
Introduction to Cellulite
Cellulite is characterized by the nonpathological appearance of the dimpled skin surface (likened to orange peel, cottage cheese, or mattress appearance), which occurs on the thighs and buttocks. As many as 80 to 90% of women experience cellulite dimpling at some point in their life. The relief alterations of cellulite include depressions and raised areas. The depressions are caused by retraction of the skin by subcutaneous fibrous septa, while raised areas are projections of fat and subcutaneous structures to the skin surface.
The current treatment for cellulite includes non-invasive (medical devices and collagenase-related products) and invasive options. However, their efficacy remains limited as the current treatment options can only treat cellulite temporarily. Additionally, most products would cause significant side effects after administration, including severe bruising, pain, and pigmentation, making most patients reluctant to receive them. The clinical need for cellulite treatment remains unmet.
| Existing Therapies | Non-Invasive Drugs | Non-Invasive Devices | Minimally Invasive Treatments | |
| FDA Approved Indications | Treatment of moderate to severe cellulite | Short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite | Short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite | Long-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite |
| Efficacy | 6-8% improvement in the appearance of cellulite by 2 grades at 3 weeks post-treatment | Improve cellulite appearance 12 weeks after one treatment | 1 year after treatment, increases 25% in Skin thickness and 29% in skin elasticity | After treatment, results lasting up to 2 years |
| Side Effect | Severe allergic reactions, marked bruising, pain, itching, lumps, discoloration, swelling and Immunogenicity | Pain, and other acceptable side effects at the treatment site | Pain, Redness, Swelling, Bruising, Itching, Blistering, Necrosis | swelling, tenderness, bruises |
R&D Progress
Cellulite is primarily caused by excess superficial subcutaneous fat compressing the fibrous septae under the skin, resulting in a dimpled, uneven surface appearance. CBL-514 can precisely reduce localized superficial fat through subcutaneous injection, improving the appearance of cellulite without causing fibrosis, nodules, or the post-treatment complications seen in current procedures. Side effects such as bruising or local reactions are generally mild.
CBL-514's Phase 2 study for moderate to severe cellulite (CBL-0201EFP Phase 2) met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, demonstrating statistically and clinically significant improvements with favorable safety and tolerability:
- Over 50% of participants experienced at least a 1-grade improvement in cellulite severity at 12 weeks after the final CBL-514 treatment.
- More than 95% of participants showed improved cellulite appearance, as assessed by both investigators and participants using the Global Aesthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS).
The results underscore the potential of CBL-514 as a safer and more effective treatment option for cellulite.


